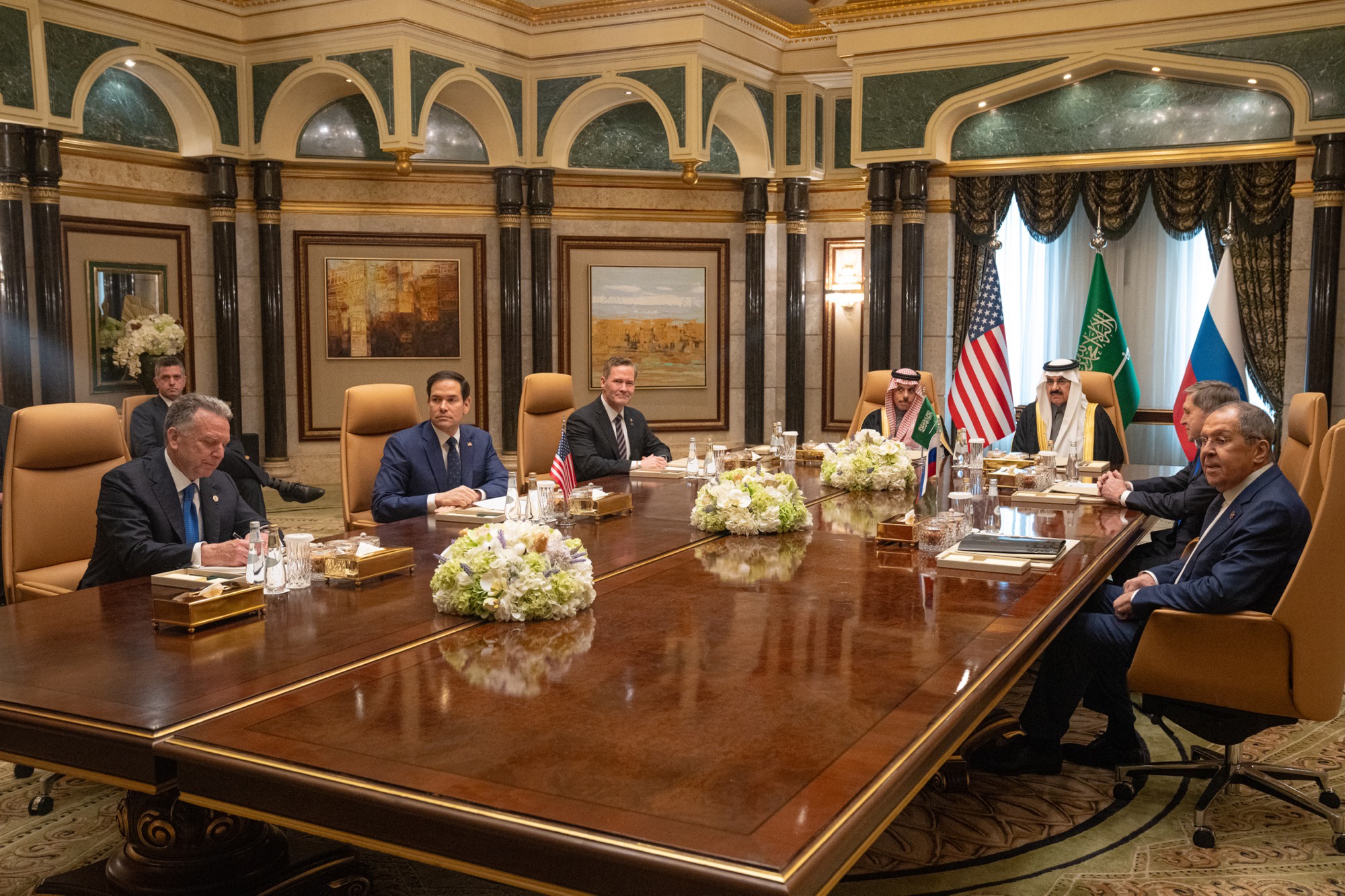
U.S.-Russian relations hit a high point during the Joe Biden administration, largely due to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. However, with Donald Trump returning to the White House, the two countries held their first high-level diplomatic and security talks in Riyadh on February 18, 2025. This meeting not only addressed bilateral relations but could also influence the direction of the Russia-Ukraine war. Picture source: Secretary Marco Rubio, February 19, 2025, X, https://x.com/SecRubio/status/1891984874627559554/photo/2.
Prospects & Perspectives No. 14
Observations on the U.S.-Russia Talks in Riyadh
By Paiku Wei
U.S.-Russia Relations Thaw After Years of Tension
U.S.-Russian relations hit a high point during the Joe Biden administration, largely due to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. However, with Donald Trump returning to the White House, the two countries held their first high-level diplomatic and security talks in Riyadh on February 18, 2025. This meeting not only addressed bilateral relations but could also influence the direction of the Russia-Ukraine war.
The talks resulted in four key agreements. Three focused on U.S.-Russia relations: (1) restoring full embassy functions and resuming ambassadorial exchanges; (2) laying the foundation for future geopolitical and economic cooperation; and (3) ensuring that bilateral relations develop efficiently and productively. The only agreement related to the Russia-Ukraine peace process was the formation of special task forces from both sides to facilitate negotiations in a “sustainable, acceptable, and beneficial to all parties” manner. Notably, Ukraine and the European Union were not invited to participate in the talks.
U.S.-Russia Relations Take Priority Over Ukraine
Initially, observers expected the meeting to set a framework for Russia-Ukraine peace talks. However, discussions focused more on U.S.-Russia relations than on specific arrangements for a peace deal.
Three key takeaways emerged from the meeting. First, Trump considers U.S.-Russia relations separate from the Russia-Ukraine war — an approach that contrasts sharply with Biden’s policies. Second, Trump prioritizes bilateral relations with major powers, emphasizing a swift restoration of ties with Russia over continued support for Ukraine. Third, his strategy is driven by economic interests, highlighting trade and investment opportunities over diplomatic concerns.
Trump’s Leadership Style: Direct and Transactional Diplomacy
Trump’s diplomatic approach reflects his characteristic personal leadership style, emphasizing efficiency and direct negotiation. He prefers speaking directly with other world leaders, whether by phone or in face-to-face meetings, rather than relying on lower-level diplomatic processes.
In his January 20, 2025, inaugural address, Trump deliberately avoided mentioning the Russia-Ukraine war. He neither expressed support for Ukraine nor condemned Russian President Vladimir Putin. Likewise, during his February 28 meeting with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy at the White House, Trump carefully refrained from making any critical statements about Putin. This move signaled goodwill toward Russia and set the stage for a potential U.S.-Russia summit.
Challenges in Reaching a Russia-Ukraine Peace Agreement
Both Ukraine and Russia have expressed interest in negotiations, and both Trump and the European Union support ending the war as soon as possible. However, each party has different expectations for a peace settlement.
Trump favors a swift agreement to reduce U.S. military and economic burdens while securing American economic interests in Ukraine. Russia seeks to solidify its territorial gains, demanding that Ukraine withdraw its forces from Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson. Additionally, Moscow insists that Ukraine abandon its NATO ambitions, adopt a neutral stance, and undergo “denazification” — the latter based on the spurious claim that the Zelenskyy regime was riddled with Nazis.
On the other hand, Ukraine and the EU have advocated for a fair and lasting peace. They argue that any agreement must respect Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity and ensure that military aggression is not rewarded, to prevent similar conflicts in future.
Although both the U.S. and the EU support Ukraine, France and Germany are more cautious than the U.S. in considering peace negotiations. They worry that a rushed ceasefire agreement could undermine European security.
The ‘Reverse Kissinger Triangle’ Strategy
The Trump administration views China as its primary global competitor and sees Russia as a potential counterbalance. By improving U.S.-Russia relations, Washington ostensibly aims to weaken the growing China-Russia alliance. This strategy mirrors the Cold War-era policies of Henry Kissinger, who engaged with China to contain the Soviet Union, but in reverse — Washington is now attempting to bring Russia closer to the U.S. in order to contain China.
Trump’s key foreign policy appointees — including his National Security Advisor Mike Waltz, Secretary of State Marco Rubio, and Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth — are all known for their hardline stance on China, indicating a potentially confrontational approach toward Beijing.
Additionally, Trump’s firm position during his meeting with Zelenskyy suggests a strategic shift. One possible explanation is that he is pressuring Ukraine into peace talks so that the U.S. can redirect military resources to East Asia. Another possibility is that Trump is first seeking to improve relations with Russia in order to fracture the growing China-Russia alliance, ultimately pursuing a “Reverse Kissinger Triangle” strategy to counter China’s influence.
In 2017, during his first term, Trump sought to improve ties with Russia to create a counterweight to China. However, the “Russiagate” controversy disrupted his plans. Although he met with Putin in Helsinki in 2018, his strategy to align with Russia against China never materialized.
From Washington’s perspective, drawing Russia closer (or at least weakening Moscow’s ties with Beijing) serves U.S. strategic interests. If a Russia-Ukraine peace deal can be reached quickly, U.S. military aid currently directed toward Ukraine could be redirected to East Asia. This suggests that Trump is highly motivated to facilitate a settlement that allows the U.S. to conserve resources for confronting China.
MAGA vs. MRGA: Nationalism as a Common Ground
The Riyadh talks marked a significant thaw in U.S.-Russia relations, moving away from the Cold War-style hostility seen under Biden. In terms of governance philosophy, Trump and Putin share similarities — both are strong nationalists who aspire to restore their countries’ past greatness.
Trump’s “Make America Great Again” (MAGA) vision prioritizes American interests and seeks to restore U.S. global leadership. Similarly, Putin’s “Make Russia Great Again” (MRGA) agenda aims to reassert Russia’s role on the international stage.
Recent developments suggest increasing willingness for U.S.-Russia cooperation. On February 24, 2025, during a United Nations General Assembly vote on an Ukraine-related resolution, the U.S. unexpectedly joined Russia in voting against it — breaking from its European allies. Additionally, both countries have signaled interest in cooperating on nuclear arms reduction and the Iran nuclear issue. Trump has even proposed renegotiating a nuclear deal with Iran, with Russia acting as a mediator in trilateral talks.
Conclusion: Uncertainty and Global Implications
Although U.S.-Russia relations appear to be improving, skepticism remains among U.S. Democrats, who continue to view Russia as a geopolitical adversary. Whether this diplomatic thaw is a long-term shift or simply a short-term Trump maneuver remains unclear.
Meanwhile, China and Russia have significantly strengthened their ties in recent years through multiple energy agreements and frequent joint military exercises. This raises doubts about whether Washington can successfully drive a wedge between Moscow and Beijing.
Additionally, if Trump’s Russia-Ukraine peace deal follows expectations — requiring Ukraine to cede territory without receiving security guarantees — it could effectively reward military aggression. A “land-for-peace” precedent would risk emboldening other expansionist leaders, including Chinese President Xi Jinping. Notably, Putin has justified his invasion of Ukraine by claiming historical ties — an argument reminiscent of China’s territorial claims over Taiwan. Therefore, Taiwan must closely monitor the evolution of the Russia-Ukraine peace process. The geopolitical consequences could directly affect security dynamics in the Indo-Pacific region.
(Dr. Wei is Associate Professor, Institute of Russian Studies, National Chengchi University)